QuantBites Weekly Newsletter
Sixth Edition of Weekly Newsletter: Global cryptocurrency regulations advance; Taurus tokenizes SME loans; S&P assesses stablecoins; BlackRock-SEC ETF talks; Norway expands CBDC research.
In this newsletter, we delve into the realms of blockchain, digital economic policies, and noteworthy advancements in science and technology. Our focus is on delivering content that truly matters, eliminating the need to sift through multiple websites and news channels. We offer two editions, one weekly and one monthly, with ongoing evolution based on your feedback.
As we grow, we have plans to introduce content in the quantitative finance domain, tailored to our readers' preferences. Until then, we invite you to enjoy our curated newsletter, bringing you the essential updates in the world of blockchain, digital economics, and cutting-edge science and technology.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
Blockchain And digital currency 💻💰
Scientific advancements 🧪⚙️
1. BLOCKCHAIN AND DIGITAL CURRENCY
Global Momentum: Over 40 Countries Advance Cryptocurrency Regulations in 2023
In a significant global development, more than 40 countries have actively pursued cryptocurrency regulations in 2023, as revealed by a PriceWaterhouseCoopers (PwC) report. The report identifies key areas of focus, including stablecoin regulation, compliance with the Financial Action Task Force's travel rule, licensing, and crypto framework development. Interestingly, compliance with the travel rule emerged as the most widely discussed issue, with 40 out of 42 jurisdictions engaging in related discussions. While some nations, such as Japan and EU states, embraced comprehensive approaches across all regulatory aspects, others, like Uganda, India, and Brazil exhibited a more selective stance. The report underscores the ongoing global efforts to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring regulatory safeguards in the evolving cryptocurrency landscape. Concurrently, Consensus 2024, a premier crypto event set for May in Austin, Texas, has attracted over 50 sponsors, highlighting the industry's collaborative momentum and growing interest in shaping its future.
Deutsche Bank-Backed Taurus Helps Tokenize SME Loans for Teylor
Swiss firm Taurus, supported by Deutsche Bank and other major players, collaborates with SME credit company Teylor to tokenize a portfolio of SME loans. Teylor, with a history of processing €3 billion in SME debt, is using Taurus's platform to make its credit portfolio tradable. This move aims to attract high-net-worth individuals and family offices by fractionalizing the investment. Teylor's decision to tokenize allows for broader accessibility and increased liquidity in the SME loan market. The process is streamlined through Taurus's regulated marketplace, Taurus TDX, which handles the distribution of principal and interest to investors on a monthly basis. Taurus, having integrated with key banking systems, emphasizes its role in providing effective tokenization solutions and digital asset custody technology.
S&P Global Ratings Launches Stablecoin Stability Assessment
S&P Global Ratings has introduced a stablecoin stability assessment, evaluating a stablecoin's ability to maintain value relative to fiat currency. This move aligns with S&P's commitment to support traditional finance (TradFi) and decentralized finance (DeFi). The assessment, rated on a scale of 1 to 5, analyzes asset quality risks, overcollateralization, governance, legal framework, redeemability, technology, and track record.
Eight Leading Stablecoins Evaluated:
The assessments include DAI, FDUSD, FRAX, GUSD, USDP, USDT, TUSD, and USDC. Ratings range from 2 (strong) to 5 (weak), with asset quality being a critical factor. Weaker aspects in regulation, governance, transparency, liquidity, and track record contributed to lower ratings.
Stablecoin Stability Assessment Highlights:
DAI, FDUSD, USDT rated 4 (constrained), FRAX, TUSD rated 5 (weak), and GUSD, USDP, USDC rated 2 (strong). Stablecoins play a crucial role as a bridge between digital and real-world assets in financial markets. The assessment is a response to market demands for transparency and insight into stablecoin risks.
BlackRock and SEC in Talks Over ETF Listing Rules
In a recent meeting, BlackRock, Nasdaq, and the SEC delved into crucial rule changes needed for the listing of a spot bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF). The spotlight is on Nasdaq's proposed rule change to trade iShares Bitcoin Trust shares, marking a pivotal moment in the crypto space.
Analysts predict a bullish surge for Bitcoin, possibly reaching $160,000 in 2024. Factors like anticipated demand from U.S. spot ETFs, the upcoming reward halving, and favorable market conditions fueled by lower interest rates are expected to propel Bitcoin to at least $50,000 in the short term.
MicroStrategy's Michael Saylor emphasized the monumental impact of spot Bitcoin ETFs, calling it potentially the most significant development on Wall Street in three decades. With these ETFs, mainstream investors now have a seamless entry point into the crypto market, akin to the game-changing introduction of the S&P 500 ETF. Get ready for a transformative shift as Bitcoin takes center stage in 2024.
Norway plans to expand its CBDC research to include wholesale , with a final decision expected in the latter part of 2025
Norway's central bank, Norges Bank, is cautiously navigating the realm of central bank digital currency (CBDC). In its recent update, the bank dismissed the need for a retail CBDC at present but hinted at potential triggers for future action. Concerns include the rise of cryptocurrencies, foreign stablecoins, and the influence of BigTech in payments. Interestingly, the bank is exploring a wholesale CBDC for interbank settlement of tokenized deposits. Facing the complexity of CBDC infrastructure, Norges Bank even contemplates leveraging the digital euro infrastructure. Despite reservations, it hopes for more suitable off-the-shelf CBDC solutions by the end of its fifth phase in 2025. The evolving landscape suggests that the digital future of currency is still under careful consideration in the land of the Northern Lights.
2. SCIENTIFIC ADVANCEMENTS
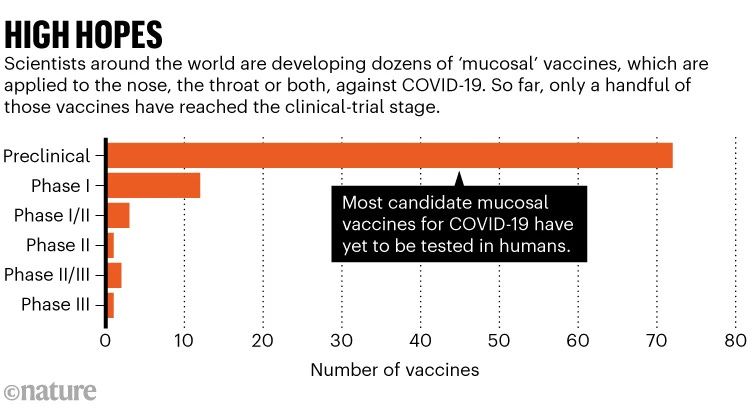
Inhaled COVID Vaccines Show Promise in Halting Infections, Monkey Trials Indicate
In a groundbreaking development, studies on monkeys reveal that delivering COVID vaccines directly to the lungs and nose can effectively halt SARS-CoV-2 infections. The findings boost the prospects of 'mucosal' vaccines administered through the nose or mouth, offering insights into potential enhancements. While traditional intramuscular vaccines excel in preventing deep lung infections, they fall short in other airway regions. Mucosal vaccines aim to stimulate immune responses in the respiratory tract's mucous membranes, providing localized protection. Recent trials involving monkeys demonstrated that delivering vaccines to the trachea or lungs produced stronger mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2. The results inspire hope for mucosal vaccines capable of achieving 'sterilizing' immunity, preventing infection entirely. Researchers anticipate continued advancements in mucosal vaccine development, potentially revolutionizing responses to respiratory viruses.
Key Points:
Traditional COVID jabs offer limited protection against infection, prompting exploration of mucosal vaccines.
Monkey trials indicate that delivering vaccines to the trachea or lungs enhances mucosal immunity and prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Mucosal vaccines could offer 'sterilizing' immunity, blocking infection entirely.
Challenges include optimizing vaccine formulations and developing effective delivery devices.
The burst of interest in mucosal vaccines extends beyond COVID-19, holding potential for addressing other respiratory viruses.
The Paradox of False Information: Surprising Ways Your Google Searches Might Deceive You
Ever wondered if Googling to fact-check false news helps? Surprisingly, a recent Nature study flips the script. Instead of reducing belief in misinformation, searching online to verify actually makes people more likely to buy into false content. New York University’s Center for Social Media and Politics led the research, unveiling that this odd outcome is linked to search-engine outputs. For users given lower-quality information, the belief in false news shoots up. The study raises concerns about "data voids," areas dominated by unreliable information. In a world where we're encouraged to fact-check, this study suggests that blindly trusting search results might lead us down a rabbit hole of misinformation. So, next time you're Googling, be cautious—it might not be the truth you find at the top of the search results.
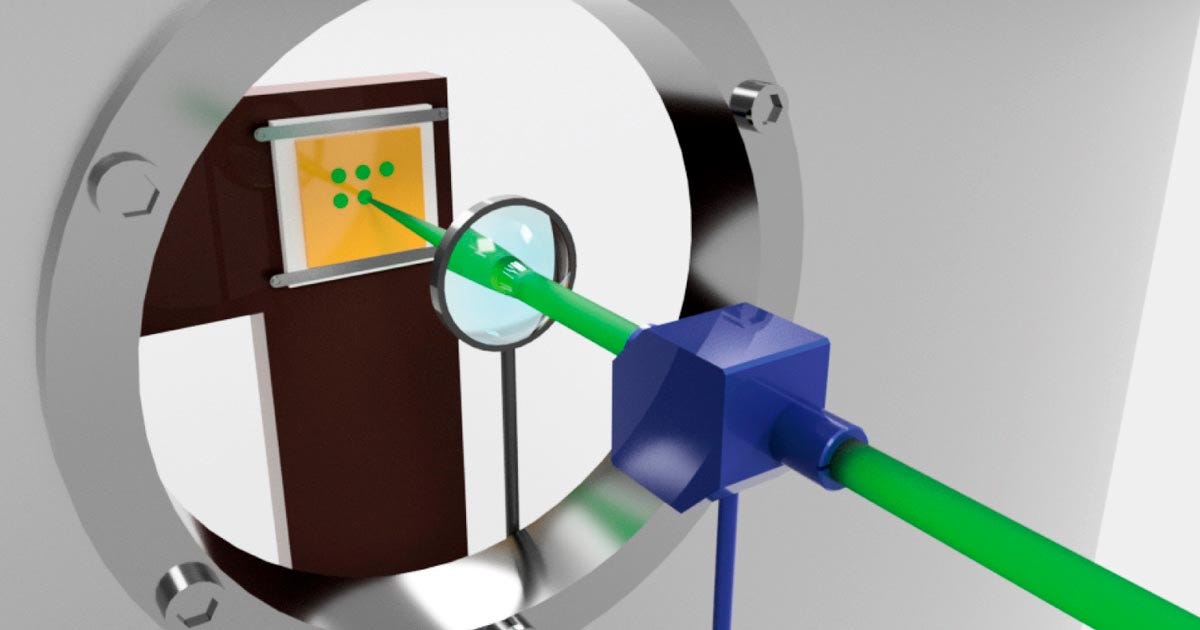
Laser-Propelled Advancement: Innovative Magnetic Devices Enabling Light Control
In a pioneering move for optical communication, a Japanese research team has cracked the code on integrating transparent magnetic materials into optical circuits. Researchers from Tohoku University and Toyohashi University of Technology utilized a groundbreaking laser heating technique to create transparent magnetic materials, overcoming a longstanding challenge in the field.
Laser-based Heating Arrangement for Fabricating a Transparent Magnetic Material.
The key to their success lies in crafting 'Cerium-substituted Yttrium Iron Garnet (Ce:YIG)'—a transparent magnetic material—using a specialized laser heating method. This addresses the hurdle of seamlessly integrating magneto-optical materials with optical circuits without causing damage, a roadblock in miniaturizing optical communication devices. This innovation opens doors for advanced optical technology, promising more efficient and compact optical communication devices in the near future.
Harvard Team Reaches Significant Milestone in Error Correction, Paving the Way for the Future of Quantum Computing
Harvard's quantum wizards are breaking through the barriers that held back quantum computing from going big! Led by Professor Mikhail Lukin, they've cracked the code on quantum error correction, a puzzle that stumped even the brainiest scientists. Imagine a quantum computer like a supercharged speedster, but with a tendency to make mistakes. Harvard's team, in collaboration with MIT and QuEra Computing, created a mind-blowing setup with laser-trapped rubidium atoms that act as super-smart bits, or "qubits." The kicker? They can rearrange these atoms on the fly during calculations. It's like a quantum dance party where errors are practically non-existent.